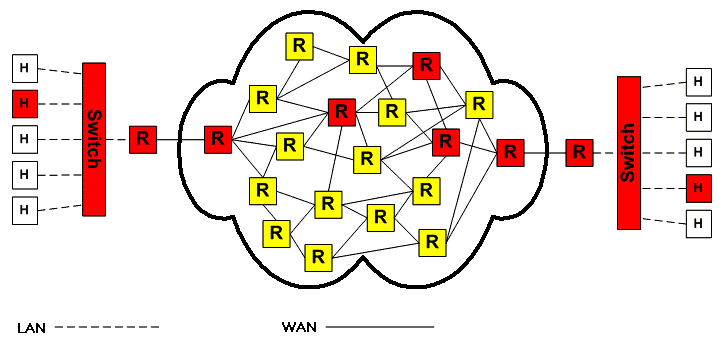

We see that the client host requesting a service is on a local area network (LAN), which connects through a switch to a router that connects to the wide area network (WAN). Packets are passed across the Internet to the server, which is a host on a different LAN.
The Internet Protocol (IP) is used to route the packets between the LANs, and the data link layer is used for moving information between two hosts within the same LAN. The two main data link functions are:
The physical layer standards spell out the physical characteristics of the medium, for example radio, optical fiber or twisted pairs of copper wire, and the way "one" and "zero" bits are signaled (the modulation method).
Most LANs today use the Ethernet data-link protocol and either a twisted pair of copper wires (CAT 5 cable) or a wireless WiFi connection at the physical layer.
The lower two layers, data-link and physical, are often discussed together as a combined network-access layer.