|
1. Call netstat with the -o switch set. That -o switch causes netstat to display process IDs (PIDs). We see that no TCP sessions are active.
2. Call netstat again, just after visiting Google. Using Internet Explorer to visit Google established an active TCP session. The Local Address is my portable computer on port 2443 and the Foreign Address, 66.102.7.104, is the Web (http) server at Google. The PID is 2796.
3. Call netstat again with the -n switch set. The -n switch displays the listening port numerically. Port 80 is the standard port for http servers.
4. Call netstat after some time. The TCP session with Google has timed out. |
C:\Documents and Settings\pressl>netstat -o Active Connections Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID C:\Documents and Settings\pressl>netstat -o Active Connections Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID TCP LPNewPortable:2443 66.102.7.104:http ESTABLISHED 2796 C:\Documents and Settings\pressl>netstat -no Active Connections Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID TCP 192.168.111.4:2443 66.102.7.104:80 ESTABLISHED 2796 C:\Documents and Settings\pressl>netstat -no Active Connections Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID |
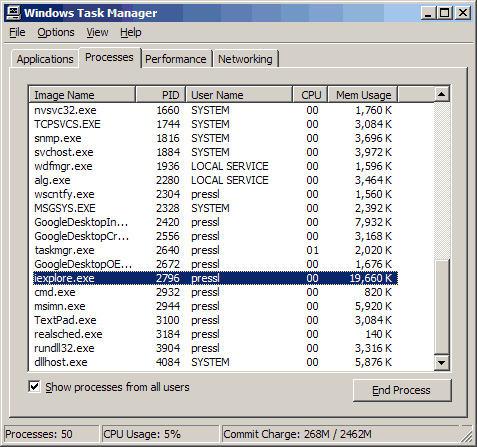
After using netstat, I was curious as to which process had the PID 2796. The Windows Task Manager showed that it was iexplorer.exe. (One executes the Task Manager by typing ctrl-alt-delete).
