Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim strName As String
strName = InputBox("What is your name?")
MsgBox("Thanks, " & strName & ". I have been waiting weeks for someone to do that.")
End Sub
In this example, the InputBox function has one argument, a string that is used to prompt the user. The function returns whatever the user enters. (If the user clicks on the cancel button, a string of length zero is returned).
The MsgBox function also has one argument in this example. It is a string to be displayed in the message box.
The InputBox function requires at least one argument (the prompt), but it has 4 optional arguments. The optional arguments are a title (string), a default input value (string), and X and Y coordinates (numeric) that determine the position of the input window on the screen.
For example, this program:
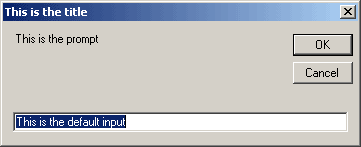
Dim strUserIn As String
strUserIn = InputBox("This is the prompt", "This is the title", "This is the default input", 1, 1)
produces this InputBox in the uppler left corner (1, 1) of the screen:

Similarly, the MsgBox function requires one argument, a string with the message, but has 2 optional arguments, a numeric code that indicates which buttons to display on the message box and a string title for the message box.
The button code is most interesting. Using it, you can put OK, Cancel, Retry, and other buttons on the message box, The following are some of the allowable button code values:
| Code | Buttons displayed |
|---|---|
| 0 | OK (the default) |
| 1 | OK and Cancel |
| 2 | Abort, Retry, and Ignore |
| 3 | Yes, No, and Cancel |
| 4 | Yes and No |
| 5 | Retry and Cancel |
You can experiment with these and check the online help for other MsgBox options.
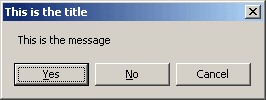
For example, this program:
Dim intButton As Integer
intButton = MsgBox("This is the message", 3, "This is the title")
produces this InputBox:
If there are multiple buttons on a message box, the programmer might also want to know which one the user clicked. The following table shows the values the MsgBox function can return:
| The user clicked | Value returned |
|---|---|
| OK | 1 |
| Cancel | 2 |
| Abort | 3 |
| Retry | 4 |
| Ignore | 5 |
| Yes | 6 |
| No | 7 |
Finally, we should note that the Show method of the MessageBox class may be used as an alternative to the MsgBox function. For example, the following statement displays a MessageBox with a greeting:
MessageBox.Show("Hiya kids, Hiya! Hiya!")
Like the MsgBox function, the Show method returns a value that can be tested later in the program to see which button the user had clicked on, for example:
Dim bob As Integer
bob = MessageBox.Show("Hiya kids, Hiya! Hiya!")