The name, data type and an optional initial value of each variable is specified with a Dim statement.
Dim <variable name> as <data type> [= <expression>]You can think of the computer as constructing the variable when the Dim statement is executed. It sets aside space in memory to hold it's value. (The amount of memory it needs to set aside depends upon the data type).
For example, consider the following Dim statements:
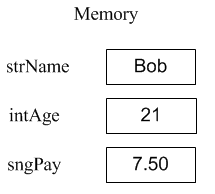
Dim strName As String = "Bob" Dim intAge As Integer = 21 Dim sglPay As Single = 7.50
When the computer executes these instructions, it would construct three variables, setting aside space in memory for each and assigning it the appropriate initial value:

We made up variable names that indicate the data type (str, int, sgl) and the meaning (name, age, pay rate). A variable name may be nearly anything you wish, but words that have specific meaning in Visual Basic, like "Dim" or "CInt," are reserved words (or Keywords) and cannot be used as variable names.
Note that the syntax of the Dim statement indicates that expression giving the initial value is optional. If it is not specified, numeric variables are assigned an initial value of zero (0) and string variables are assigned an initial value of Null ("").