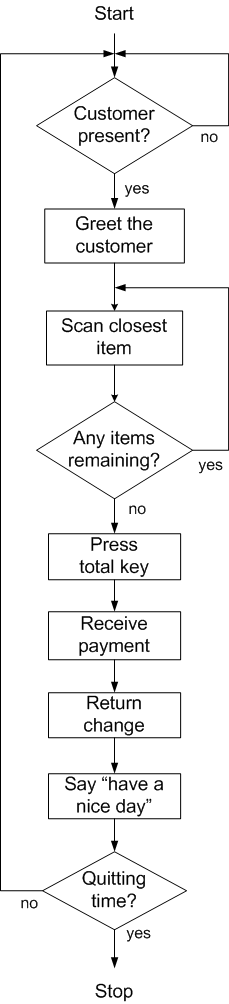
Checkout stand algorithm with loops
This flowchart shows an algorithm for a cashier at a supermarket checkout stand. It has three loops. Each loop has a body and a termination condition. The body is executed repeatedly until the termination condition is satisfied. Once it is satisfied, the loop terminates and execution continues with the next sequential instruction.
Note that two of the loops are nested inside the outer loop